Introduction
Pile foundations are one of the most important deep foundation solutions in civil engineering. They transfer heavy structural loads deep into the ground, bypassing weaker soil layers near the surface. This makes them essential for buildings, bridges, towers, and marine structures.
In India, where soil conditions vary drastically from state to state, understanding when to use pile foundations and where they are most suitable is vital for safe, durable, and cost-effective construction.
This guide will cover:
- What is a pile foundation?
- Types of pile foundations
- Situations where pile foundations are used
- Locations and soil conditions where they are most effective
- Advantages and limitations
- FAQs for quick reference
What is a Pile Foundation?
A pile foundation is a deep foundation system made of long, slender columns, usually made from concrete, steel, or timber. These piles are driven, bored, or cast into the ground to reach strong soil or rock layers.
Key purposes of pile foundations:
- Transfer loads to deeper, stronger soil strata.
- Resist uplift forces in tall structures or towers.
- Provide stability in loose, waterlogged, or expansive soils.
Types of Pile Foundations
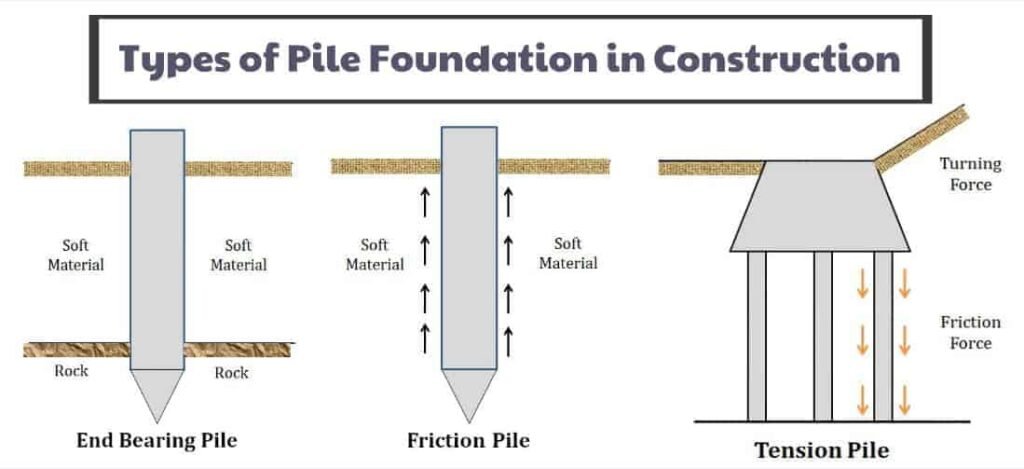
| Type of Pile | Material | Key Function | Common Usage in India |
|---|---|---|---|
| End Bearing Piles | Concrete, Steel | Transfer load directly to strong strata | High-rise buildings in urban cities |
| Friction Piles | Concrete, Timber | Transfer load through skin friction | Coastal areas with deep soft clay |
| Bored Cast-In-Situ Piles | Reinforced Concrete | Formed on-site by drilling and concreting | Bridges, flyovers, metro projects |
| Driven Piles | Steel, Concrete | Precast and hammered into place | Port structures, offshore projects |
| Sheet Piles | Steel, Timber | Provide earth retention and water cutoff | River embankments, basements |
| Micro Piles | Steel, Concrete | Small-diameter piles for confined spaces | Old building retrofitting |
Also Read How to Calculate the Volume of Trapezoidal Footing: Step-by-Step Guide for Civil Engineers
When to Use Pile Foundations
You should consider using pile foundations in the following cases:
1. Weak Surface Soils
If the top layers of soil are too soft, loose, or compressible, shallow foundations like isolated footings may fail. Pile foundations bypass these layers and transfer loads to deeper, stable layers.
Example: Construction in Kolkata’s alluvial soils or Delhi’s Yamuna floodplain.
2. High Structural Loads
Large commercial complexes, skyscrapers, and industrial plants exert heavy loads that shallow foundations cannot safely bear.
Example: Metro stations in Mumbai where buildings have high column loads.
3. Coastal and Marine Construction
In waterlogged areas or where soil has poor bearing capacity, piles are driven into dense sand or rock below the seabed.
Example: Port terminals in Chennai or fishing harbours in Kerala.
4. Bridge and Flyover Piers
Bridges require stable foundations in rivers, where scour and erosion are major risks. Piles provide the necessary depth and stability.
5. Sites with Expansive or Shrinkable Soil
In regions with black cotton soil like parts of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh, piles transfer loads below the seasonal shrink-swell zone.
6. Structures Subjected to Uplift or Lateral Loads
Piles can resist wind uplift, earthquake loads, and lateral earth pressure, making them ideal for tall towers, chimneys, and retaining walls.
Where to Use Pile Foundations in India
| Region | Soil Condition | Recommended Pile Type | Example Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coastal Andhra Pradesh | Soft clay, saline water | Friction piles, sheet piles | Jetty construction |
| Assam River Valleys | Loose alluvial sand | Bored cast-in-situ piles | River bridges |
| Mumbai Metropolitan Region | Reclaimed land, loose fill | End bearing piles | High-rise towers |
| Kerala Backwaters | Waterlogged clay | Driven concrete piles | Boat jetties |
| Gujarat Coastal Belt | Silty sand | Steel driven piles | Offshore oil platforms |
Advantages of Pile Foundations
- Can be installed in water or soft ground.
- Transfer loads to great depths.
- Suitable for both vertical and lateral loads.
- Minimal vibration when bored piles are used.
- Adaptable to different soil and load conditions.
Limitations of Pile Foundations
- Higher cost compared to shallow foundations.
- Requires skilled labour and heavy equipment.
- Time-consuming in large-scale projects.
- Difficult to inspect once installed.
Step-by-Step Installation Process (Bored Pile Example)
- Site Investigation – Identify soil strata and load requirements.
- Borehole Drilling – Create a hole to the required depth.
- Casing Installation – Prevents bore collapse.
- Reinforcement Cage Placement – Provides structural strength.
- Concrete Pouring – Using tremie method for underwater concreting.
- Curing and Quality Checks – Ensures long-term durability.
Conclusion
Pile foundations are essential for construction in challenging soil conditions or when heavy loads are involved. In India, they are widely used in metro projects, high-rise buildings, ports, and bridges. Choosing the right pile type depends on soil conditions, project load, and site environment.
By understanding when and where to use pile foundations, engineers and builders can ensure safety, durability, and cost efficiency. Proper design, installation, and quality control are key to achieving long-lasting performance.
FAQs on Pile Foundations
Q1. What is the minimum depth for a pile foundation?
It depends on the soil condition, but generally, piles extend 3 to 5 meters into firm strata.
Q2. Which is better – driven piles or bored piles?
Driven piles are faster but cause vibration. Bored piles are better for sensitive urban sites.
Q3. Can pile foundations be used for small houses?
Q1. What is the minimum depth for a pile foundation?
It depends on the soil condition, but generally, piles extend 3 to 5 meters into firm strata.
Q2. Which is better – driven piles or bored piles?
Driven piles are faster but cause vibration. Bored piles are better for sensitive urban sites.
Q4. How long can pile foundations last?
If designed and constructed well, pile foundations can last over 100 years.
Q5. Are pile foundations earthquake-resistant?
Yes, if designed for seismic loads, piles can provide good earthquake performance.
Final tips and conclusion
Pile foundations are a powerful tool when soil near ground is weak or loads are heavy.
Start with a proper geotechnical investigation.
Choose the pile type that fits soil, load, environment and site constraints.
Follow IS 2911 and project-specific requirements for design, testing and quality control. SRC- Law Resource
Good planning reduces surprises and cost overruns.
In India, CFA and bored cast-in-situ piles are widely used for urban projects. Modern rigs and testing methods make piling reliable when done by competent contractors.