Shoring in construction is a temporary support technique used to stabilize structures like excavations, trenches, or unsafe walls. It prevents collapses and ensures safety during construction work. This method is essential for deep excavations, especially when working close to existing buildings or unstable soil.
Understanding the types of shoring, when to use them, and their advantages helps ensure construction safety and project success.
What is Shoring in Construction?
Shoring is a method of supporting a building, structure, or trench with props (usually made of timber, metal, or hydraulic systems) when there is a risk of collapse or during repairs or modifications.
It is widely used in:
- Deep excavation projects
- Basement construction
- Building renovations
- Trench support for pipelines or cables
- Stabilization of damaged structures
Types of Shoring in Construction Projects
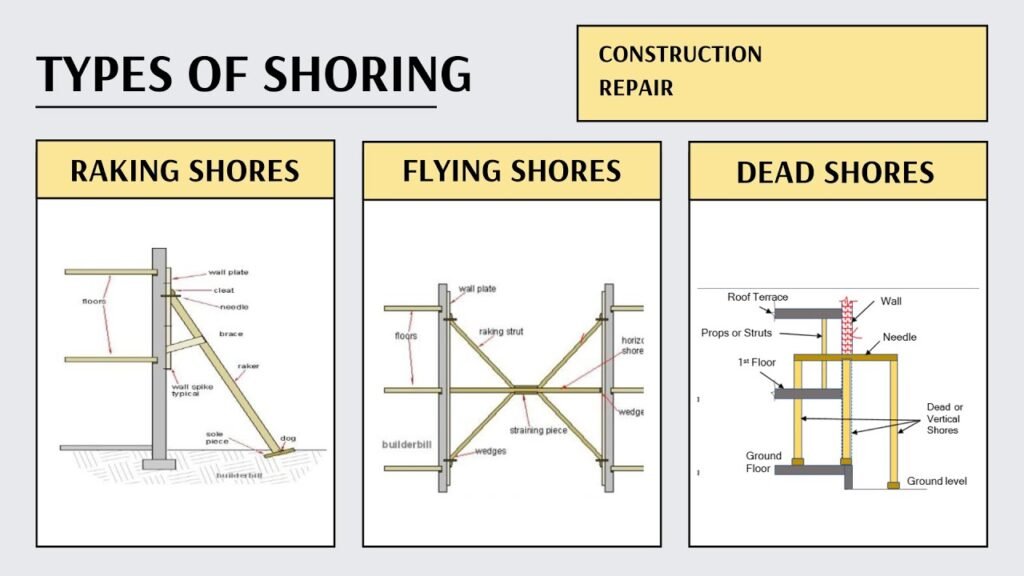
Below are the most commonly used types of shoring systems in construction in India:
1. Soldier Pile Shoring (H-Beam Shoring)
Steel H or I beams are driven vertically into the ground. Timber planks are placed horizontally between the beams to support the soil. Suitable for excavation depths up to 5 meters.
2. Secant Pile Shoring
Constructed by drilling overlapping concrete piles. Used in sites with high groundwater levels or space limitations. Offers a watertight and strong support wall.
3. Contiguous Pile Shoring (Tangent Piles)
Similar to secant piles but with minimal spacing between piles. Not watertight but faster and more economical. Ideal for dry soil conditions.
4. Sheet Pile Shoring
Interlocking steel sheets are driven into the ground to form a continuous wall. Best for excavations near water bodies or where groundwater control is essential.
5. Diaphragm Wall Shoring
A reinforced concrete wall constructed in-situ under bentonite slurry. Used for deep basement excavations, tunnels, and metro stations. Offers maximum strength and water resistance.
6. Hydraulic Shoring
This type uses hydraulic pistons to apply pressure and support trench walls. Often combined with steel or aluminum plates. Quick to install and remove.
7. Raking Shoring (Inclined Props)
Inclined supports are placed at an angle to support unstable walls. Common in building repairs or during partial demolitions.
8. Flying Shoring (Horizontal Bracing)
Horizontal support system used between two walls. Helpful when open space is required beneath the supported area.
9. Dead Shoring (Vertical Props)
Vertical timber or steel props used to support overhead loads. Often applied during the removal or reconstruction of walls.
10. Soil Nailing
Stabilizes soil by inserting steel bars (nails) into a slope or excavation face. Generally used for steep slopes, retaining walls, or roadways.
Also Read Stunning Staircase Designs for Indian Homes: Types, Features & Space-Saving Ideas
Shoring Materials Used in India

| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Timber | Cost-effective and easy to work with | Prone to rot; limited durability |
| Steel | High strength; reusable | Expensive; heavy to handle |
| Aluminum | Lightweight; corrosion-resistant | Higher cost; limited load capacity |
| Concrete | Durable; used for permanent systems | High installation cost |
When to Use Shoring in Construction?
Shoring is required in construction when:
- Excavation is deeper than 1.2 meters
- Soil is loose or water-logged
- Working near existing buildings or roads
- Building repairs or wall removal is involved
- Construction is in confined or congested urban sites
- Groundwater level is high or soil pressure is excessive
Benefits of Shoring Systems
- Ensures safety of workers and nearby structures
- Prevents soil collapse and structural failure
- Allows for deeper and safer excavations
- Reduces construction delays due to accidents
- Enables foundation or basement works in compact areas
Limitations of Shoring in Construction
- Increases overall project cost
- Requires skilled labor and planning
- Some methods need heavy machinery
- May be noisy or cause vibrations in dense areas
- Temporary; not a permanent soil retention method
Real-Life Applications of Shoring in Indian Construction
| Application | Shoring Method |
| Metro stations and tunnels | Diaphragm Wall, Secant Piles |
| Deep basement excavations | Contiguous or Soldier Pile Shoring |
| Water pipelines or trench support | Hydraulic or Sheet Pile Shoring |
| Building wall support during repair | Dead, Flying or Raking Shores |
| Road or slope stabilization | Soil Nailing and Shotcrete |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between shoring and scaffolding?
Shoring provides structural support, while scaffolding is a temporary work platform for laborers.
Q2. When is shoring necessary in construction?
It’s needed during deep excavations, wall modifications, and when working near existing structures.
Q3. What is trench shoring?
Trench shoring supports the walls of trenches to prevent collapses during pipe or cable installation.
Q4. Can shoring be reused?
Steel and aluminum shoring systems can be reused. Timber shoring is often single-use.
Q5. Is shoring mandatory for deep basements in India?
Yes, construction codes in India require proper support systems for deep excavation to ensure safety.
Conclusion: Importance of Shoring in Safe Construction
Shoring plays a key role in modern Indian construction practices, especially in high-density urban areas. Whether for deep basement works, metro tunneling, or building restoration, shoring provides safety and stability to ongoing construction tasks.
Contractors must select the right type of shoring based on soil condition, excavation depth, space constraints, and structural needs. Proper planning and supervision are essential to ensure the safety and success of shoring operations.
When executed correctly, shoring becomes a vital tool in safe excavation, foundation construction, and building renovation projects across India.










