Introduction
In building construction, footings are essential for transferring loads from the structure to the ground. Among the various types of footings, trapezoidal footings are commonly used when the soil bearing capacity varies or when the load distribution requires a stepped or sloped base. Calculating the volume of trapezoidal footing is important for estimating the quantity of concrete and preparing accurate construction cost estimates.
In this guide, we will explain the formula for trapezoidal footing volume, step-by-step calculation, and provide examples for practical use. This article is tailored for Indian construction projects with simple vocabulary and clear explanations.
What is a Trapezoidal Footing?
A trapezoidal footing is a sloped or stepped concrete footing where the top and bottom surfaces are rectangular but with different dimensions. The sides form trapezoidal shapes when viewed in cross-section.
This design helps in:
- Reducing the quantity of concrete compared to plain rectangular footings.
- Providing better load transfer in sloping soil conditions.
- Achieving economy in material usage.
Two common geometric cases and their volumes
You will usually meet these two cases on site:
- Prismatic trapezoidal footing (slope in one direction only).
- Cross section is a trapezoid.
- Volume = Area of trapezoid × Length (prism rule). SRC- theconstructor.org
- Truncated pyramid footing (frustum) (slopes in both directions).
- Top and bottom are rectangles (or squares) of different sizes.
- Volume uses the frustum (truncated pyramid) formula. SRC- Testbook
Later sections give formulas and worked examples for both.
Useful Trapezoidal formulas (quick reference)
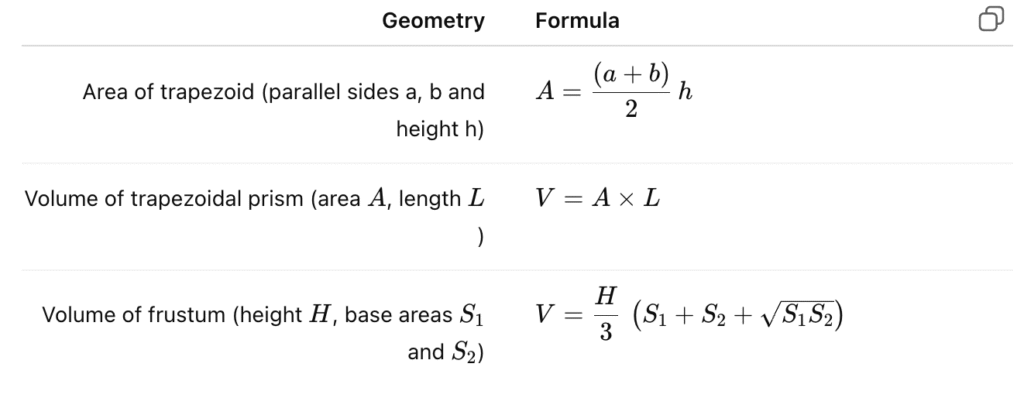
Notes: S1S_1S1 and S2S_2S2 are the areas of the two parallel end faces (for square/rectangular bases use side×side)
When to use each Trapezoidal formula on site

In many practical cases you will mix both methods – split the footing into a rectangular block plus frustum parts. Several online calculators and civil guides use this combination.
Also Read Superelevation of Roads: Meaning, Design, and Indian Best Practices
Formula for Volume of Trapezoidal Footing
The volume of a trapezoidal footing is calculated using the formula:
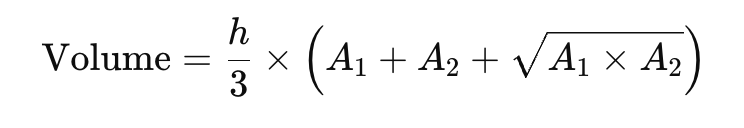
Where:
- h = depth or height of the footing (in meters)
- A₁ = area of the bottom rectangle (L₁ × B₁)
- A₂ = area of the top rectangle (L₂ × B₂)
Step-by-Step Method to Calculate Trapezoidal Footing Volume
Step 1: Measure Dimensions
- Length of bottom (L₁)
- Breadth of bottom (B₁)
- Length of top (L₂)
- Breadth of top (B₂)
- Height (h) of the footing
Step 2: Calculate Areas
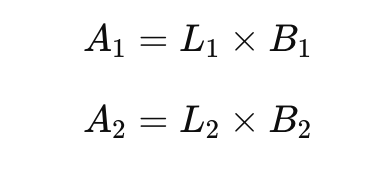
Step 3: Apply the Formula
Substitute the values into:
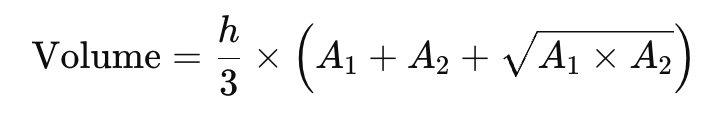
Example Calculation
Given:
- L₁ = 2.0 m, B₁ = 2.0 m
- L₂ = 1.5 m, B₂ = 1.5 m
- h = 0.6 m
Step 1:
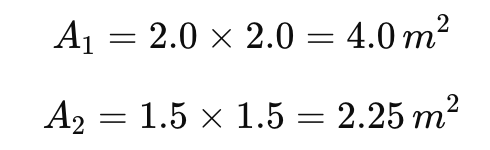
Step 2:
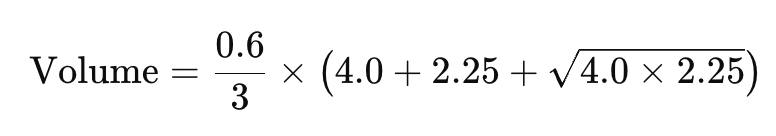
Step 3:
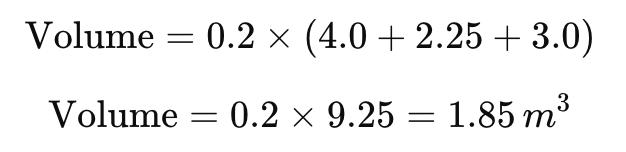
So, the required concrete volume is 1.85 cubic meters.
Table: Quick Reference for Trapezoidal Footing Volume
| L₁ (m) | B₁ (m) | L₂ (m) | B₂ (m) | Height h (m) | Volume (m³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 1.85 |
| 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 2.58 |
| 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 4.33 |
Importance of Accurate Volume Calculation
- Cost Control – Prevents wastage of concrete and ensures proper budgeting.
- Material Planning – Helps in ordering the right quantity of cement, sand, and aggregates.
- Structural Safety – Ensures the designed thickness and load capacity are met.
IS Codes Relevant to Footing and Concrete Works
To ensure that your calculations and construction practices align with industry standards, here are some key IS codes that cover footings and concrete works:
- IS 456:2000 – This code provides the general guidelines for the design and detailing of plain and reinforced concrete, covering everything from materials to safety and structure. Specifically, Clause 34.1.2 addresses the use of trapezoidal footings.
- IS 3370 – For concrete structures, including footings that are subject to liquid and water pressures.
- IS 383 – Specifications for coarse and fine aggregates used in concrete, ensuring the right quality of materials.
- IS 4926 – Guidelines for the use of ready-mixed concrete in projects, which may be relevant depending on your concrete sourcing.
These IS codes ensure structural reliability, durability, and safety by standardizing concrete and reinforcement requirements for footings and other structural elements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring slope differences between top and bottom.
- Using wrong units (e.g., mixing cm and meters).
- Forgetting to include footing projections in measurements.
FAQs on Trapezoidal Footing Volume
Q1. Why use a trapezoidal footing instead of rectangular footing?
A trapezoidal footing reduces concrete consumption while maintaining strength, making it economical for large loads and varying soil conditions.
Q2. Which unit is used for volume calculation?
Volume is generally calculated in cubic meters (m³) for civil engineering projects in India.
Q3. Can the formula be used for circular footings?
No, circular footings have a different formula based on cylinder or frustum shapes.
Q4 — How to estimate excavation volume for trapezoidal footing?
Excavation depends on soil slope and benching. For vertical cut, excavation ≈ concrete volume + clearance for formwork. For sloped cut, compute soil prism by extending slopes and using earthwork bulking factors.
Conclusion
Calculating the volume of trapezoidal footing is a crucial step in construction planning. Using the frustum formula, civil engineers can estimate the concrete requirement accurately. This improves project cost control, ensures material efficiency, and maintains structural safety.
For Indian construction projects, this calculation method ensures both economy and durability. Always verify dimensions on-site before finalizing the volume.









